MicrochipdsPIC33F離線1000WUPS電源參考設(shè)計(jì)
Digital Pure Sine Wave Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) Reference Design dsPIC33FJ06GS101/X02 and dsPIC33FJ16GSX02/X04 Data Sheet High-Performance, 16-bit Digital Signal Controllers

圖1.正弦波UPS參考設(shè)計(jì)外形圖
UPS參考設(shè)計(jì)輸入/輸出指標(biāo):
Input / Output Specifications:
Input Range AC:
95 – 135V, 60 Hz (+/ - 3 Hz) (110V version)
210 – 242V, 50 Hz (+/- 3 Hz) (220V version)
Output Voltage AC:
110V @ 60 Hz (+/ - 1 Hz) (110V version)
220V @ 50 Hz (+/ - 1 Hz) ( 220V version)
DC Input:
36V (12 VDC X 3)
Lead Acid Battery
Rating:
1000 VA Steady-State Output Power
1350 VA Peak Power (Surge)
Features:
High-frequency design
Adjustable Charging current
Efficiency of 84%
Pure sine wave output with THD 3%
Mains to Battery Transfer time 10 ms
Supports Crest Factor of 3:1
Minimum Power Factor(Leading/Lagging) of 0.65
Fault indications
USB Communication with PC
LCD front panel
An Uninterruptible Power Supply, or UPS, is an electronic device that provides an alternative electric power supply to connected electronic equipment when the primary power source is not available.
Unlike auxiliary power, a UPS can provide instant power to connected equipment, which can protect sensitive electronic devices by allowing them to shut down properly and preventing extensive physical damage. However, a UPS can only supply energy for a limited amount of time, typically 15 to 20 minutes.
Although its use can extend to a virtually unlimited list of applications, in past years the UPS has become even more popular as a means of protecting computers and telecommunication equipment, thus preventing serious hardware damage and data loss.
Types of UPS Systems
A typical UPS for computers has four basic protection roles: being able to cope with power surges, voltage shortage, complete power failure and wide variations in the electric current frequency. There are three types of UPS systems, depending on how the electric power is being stored and relayed to the electronic device connected to them:
? Offline UPS (also known as Stand-by UPS)
? Line-Interactive (or Continuous UPS)
? Online UPS (often called double conversion supply)

圖2.離線UPS方框圖
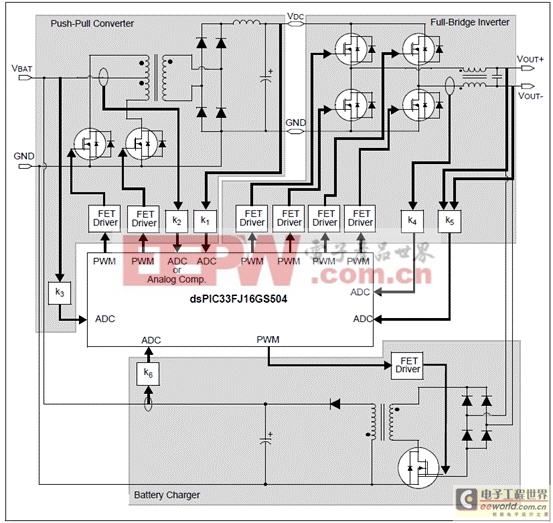
圖3.采用dsPIC33FJ16GS504的離線UPS方框圖
The reference design in this application note describes the design of an Offline Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) using a Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) dsPIC? Digital Signal Controller (DSC).
The Offline UPS Reference Design consists of three major UPS topology blocks:
? Push-Pull Converter (steps up the DC battery voltage to a constant high-voltage DC)
? Full-Bridge Inverter (converts DC voltage to a sinusoidal AC output)
? Flyback Switch Mode Charger (current source and charges battery with constant current)
1kW離線UPS主要指標(biāo):

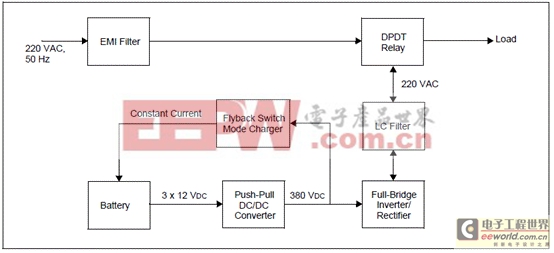
圖4.離線UPS參考設(shè)計(jì)框圖
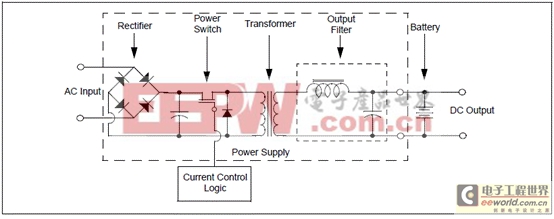
圖5.開(kāi)關(guān)模式充電器框圖

圖6.離線UPS詳細(xì)框圖

圖7.離線UPS參考設(shè)計(jì)電路圖(1)
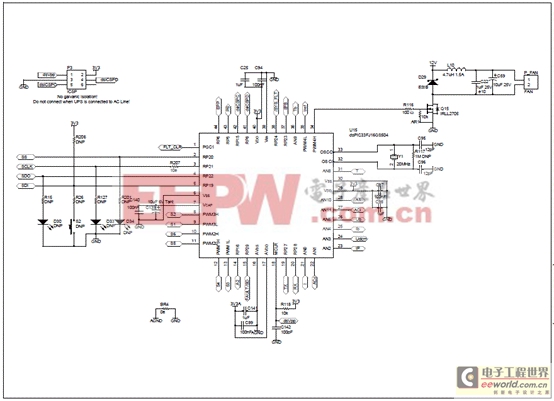
圖8.離線UPS參考設(shè)計(jì)電路圖(2)
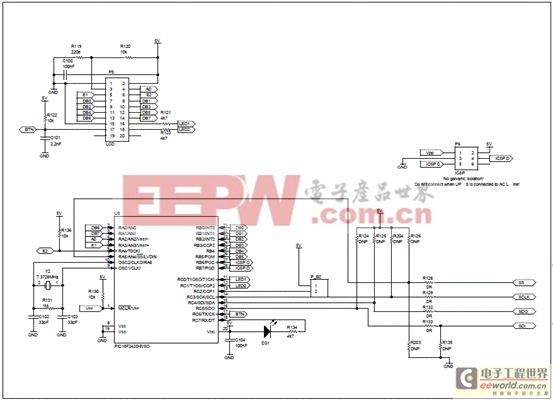
圖9.離線UPS參考設(shè)計(jì)電路圖(2)
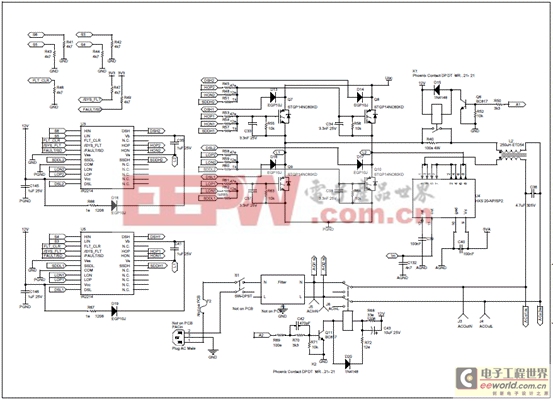
圖10.離線UPS參考設(shè)計(jì)電路圖(3)

圖11.離線UPS參考設(shè)計(jì)電路圖(4)
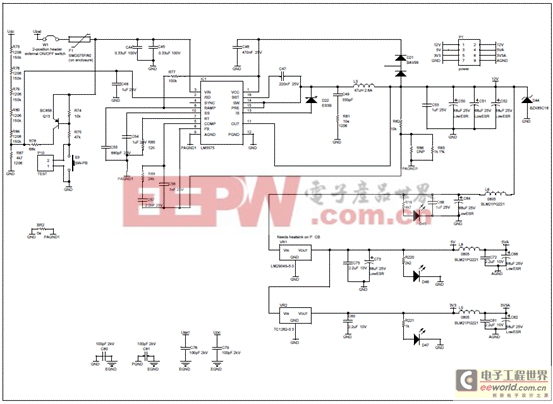
圖12.離線UPS參考設(shè)計(jì)電路圖(5)
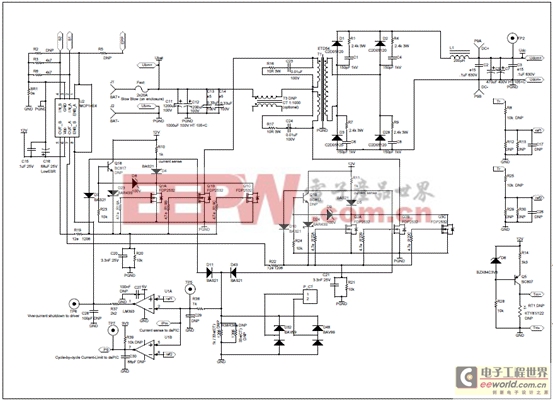
圖13.離線UPS參考設(shè)計(jì)電路圖(6)
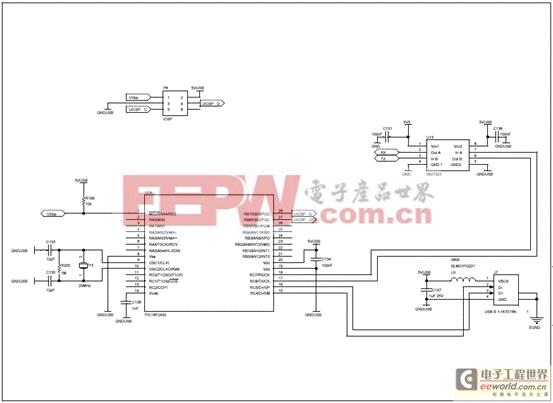
圖14.離線UPS參考設(shè)計(jì)電路圖(7)
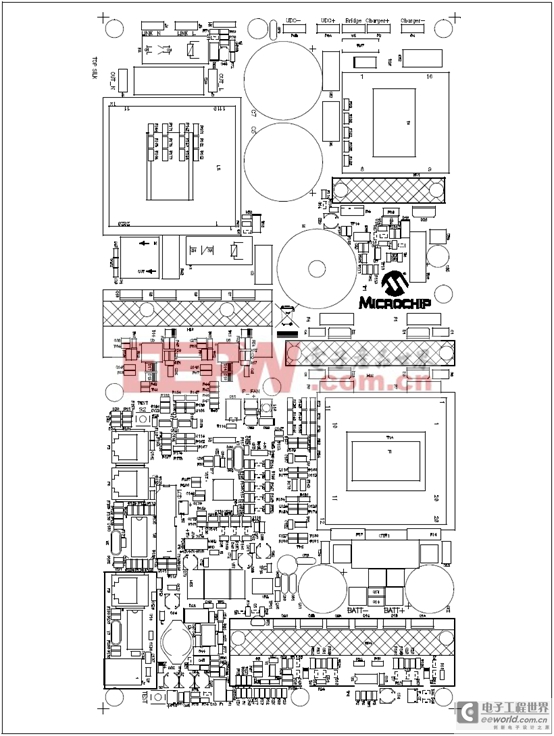
圖15.離線UPS參考設(shè)計(jì)PCB布局圖(頂層)
詳情請(qǐng)見(jiàn):
http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/70318D.pdf
和
http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/AppNotes/01279B.pdf




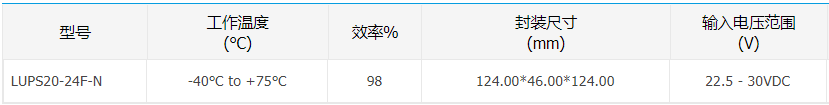









評(píng)論